Pengertian
Direct Speech
- Direct Speech atau Quoted Speech atau Kalimat Langsung merupakan kalimat yang berisikan informasi dari pembicara yang ditulis apa adanya.
- Ciri-ciri dari direct speech adalah
- adanya tanda kutip (“…”) atau (‘…’)
- tidak terdapat kata hubung (conjunction)
- contoh:
- Emily telah berkata, “saya capek”.
- Emily has said, “I am tired”.
Indirect Speech
- Indirect Speech atau Reported Speech atau Kalimat Tak Langsung merupakan kalimat yang berisikan informasi dari pembicara yang tidak ditulis apa adanya.
- Ciri-ciri dari indirect speech adalah
- Tidak terdapat tanda kutip (“…”) atau (‘…’)
- terdapat kata hubung (conjunction)
- contoh:
- Emily telah berkata bahwa dia capek.
- Emily has said that she is tired.
Note
- Jika terdapat conjunction seperti pada contoh Indirect speech, maka klausa yang tidak mengandung conjunction disebut dengan main clause (MC), dan klausa yang mengandung conjunction disebut dengan subordinate clause (SC)
contoh:- Ethan said, “I am fat”
- Ethan said that I was fat.
MC SC
- Kata tell, ask, say … disebut sebagai introductory verb atau verb yang menghubungkan main clause dengan subordinate clause
- Main clause dapat diletakkan di akhir dan bisa ditukar asalkan subject nya bukan pronoun.
- Contoh:
- Ethan said, “I am fat.”
- “I am fat”, Ethan said.
he - “I am fat”, said Ethan.
he
Macam dan Aturan Perubahan
Terdapat tiga macam DS-IS dan aturan perubahannya, yaitu statement, Imperative, dan Question. Pada artikel ini akan dibahas macam DS-IS yang pertama yaitu statement, berikut ini merupakan penjelasannya.
Statement
- merupakan bentuk pernyataan
- conjunction yang digunakan adalah that (bahwa)
- aturan perubahan
- perubahan tenses
- perubahan pronoun
- perubahan adverb
Perubahan Tenses (Direct Speech ke Indirect Speech)
- Perubahan hanya pada SC
- MC bertenses Simple past tense
- tenses mundur 1 kali
misal: dari tense simple present mundur ke simple past dan kemudian ke simple perfect (Perhatikan gambar dibawah ini)
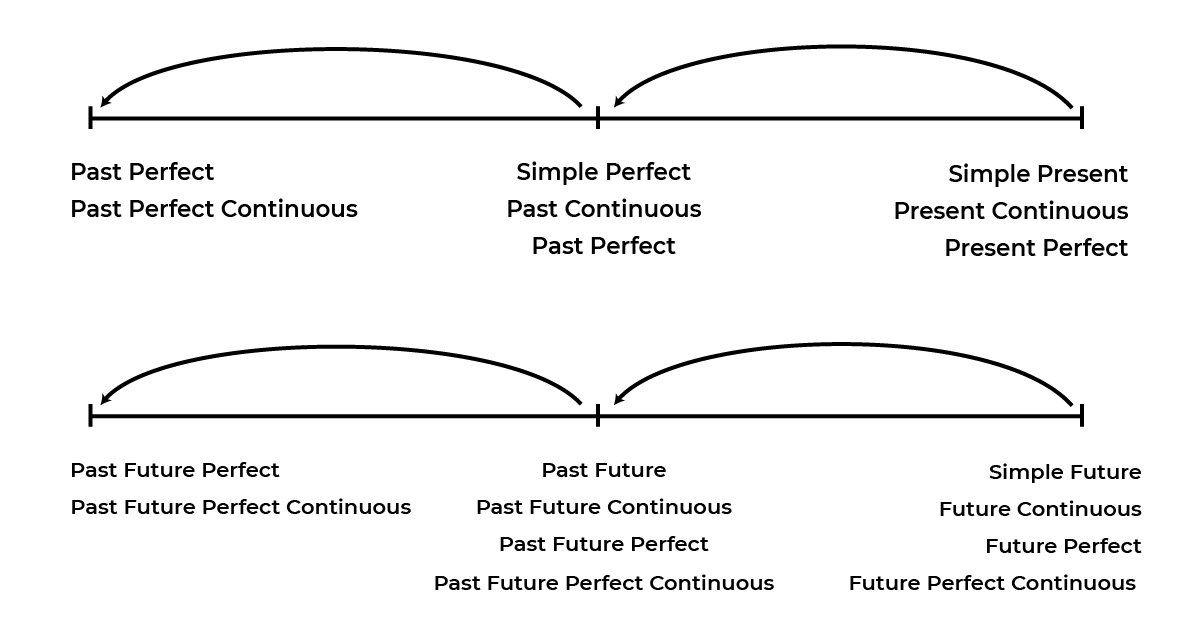
- contoh kalimat
- DS : Emily said, “Ethan is sick.“
simple present - IS : Emily said that Ethan was sick.
simple past - DS : Clark said, “Charles has eaten.”
present perfect - IS : Clark said that Charles had eaten.
past perfect
- DS : Emily said, “Ethan is sick.“
Note
- tenses dalam SC tidak berubah jika
- I.V (introductory verb) tidak menggunakan tense simple past
contoh:- DS : Emily has said, “Ernie is happy.”
- IS : Emily has said that Ernie is happy.
- SC menunjukkan kebenaran umum
contoh- DS : Catherine said, “The fire is hot.”
S.past kebenaran umum - IS : Catherine said that the fire is hot.
tidak berubah
- DS : Catherine said, “The fire is hot.”
- I.V (introductory verb) tidak menggunakan tense simple past
Perubahan Pronoun
Aturan perubahan pronoun adalah sebagai berikut:
- Jika terdapat pronoun I, my, me, mine … , maka kembali ke subject MC.
contoh:- DS : Emily said, “My mother likes my bike.”
- IS : Emily said that her mother liked her bike.
- Jika terdapat pronoun you, your, yours, … , maka kembali ke object MC (jika MC tidak mempunyai object, maka object nya adalah me.
- DS : Ethan said to Emily, “I love you.”
- IS : Ethan said to Emily that he loved her.
- Jika terdapat pronoun we, us, our, ours …, maka tetap we jika speaker termasuk we, dan berubah menjadi they jika speaker tidak termasuk dalam we.
contoh:- DS : Emily and Ethan said, “we will marry.”
- IS : Emily and Ethan said that they would marry.
Perubahan Adverb
Aturan perubahan adverb adalah sebagai berikut:
- syarat → sama dengan perubahan tenses
- aturan
| Adverb (DS) | Adverb (IS) |
| now
yesterday tomorrow next week last week 2 days ago 2 days later today |
then
the day before/the previous day the day after/the following day the week after the week before 2 days before 2 days after that day |
contoh:
- DS : Ethan said to Emily, “I am waiting for you now.”
- IS : Ethan said to Emily that he was waiting for her then.
- DS : Emily said, “I met Sue yesterday.”
- IS : Emily said that she had met Sue the day before.
- DS : Ethan said, “I will marry her next year.”
- IS : Ethan said that he would marry her the year after.
Latihan Soal
Exercise 1

Tentukan termasuk DS atau IS kah kalimat-kalimat di bawah ini!
Klik halaman selanjutnya untuk mengerjakan exercise berikutnya.
5
/
5
(
3
votes
)





1 thought on “Pengertian, Macam dan Aturan Perubahan, serta Latihan Soal Direct Speech – Indirect Speech (Part 1)”
It’s great’s !! we can learning and task question !! free question only login facebook !!! ut’s very good article